Blog Detail
Table of Contents

Different Types of Hearing Loss
- Amy
- Dec 9, 2024
- 0 Comments
Hearing loss can be divided into two types: conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss. The former can usually be treated by removing physical obstacles, and the latter is divided into noise-induced hearing loss and hearing loss caused by aging. In most cases, it is irreversible and can be enhanced by wearing hearing aids, cochlear implants or auditory brainstem implants to enhance hearing sensitivity.
In clinical hearing tests, clinicians use dB HL (hearing level) to measure sound intensity, which is the decibel number relative to the smallest sound that a healthy young person should be able to hear. Thresholds between -10 and +20 dB HL are the normal range.
1. Conductive hearing loss
Due to the obstruction of sound transmission to the inner ear, it may be caused by cerumen obstruction, ear infection (middle ear effusion OME) or calcification of the small bones of the middle ear (ossicular sclerosis). Conductive hearing loss tends to show a loss of sensitivity across the entire frequency range, most commonly in one ear. Bone conduction testing can be used to confirm suspected conductive hearing loss, in which sound is transmitted as vibrations through the skull rather than through the air to the ear canal.
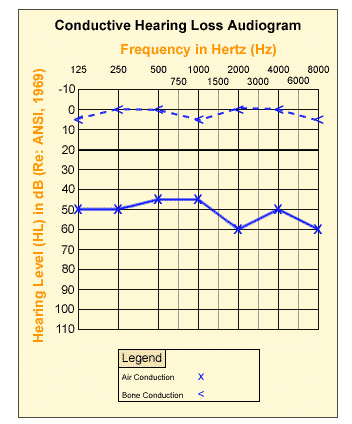
(image source: US Occupational Health Administration)
2. Sensorineural hearing loss
The most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss is damage to the hair cells in the cochlea.
In rare cases, hair cells are damaged by certain chemicals (such as high doses of aminoglycoside antibiotics). In most cases, the delicate outer hair cells are damaged by prolonged exposure to loud sounds or by aging.
(1) Noise-induced damage
The outer ear and middle ear can efficiently transmit frequencies close to 4kHz, so hair cells tuned to frequencies close to 4kHz are particularly susceptible to noise-induced damage. Therefore, the audiogram of patients with noise-induced damage often has a typical notch at 4kHz:
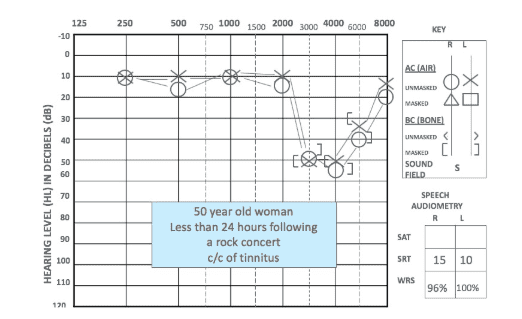
(image source: audiologyonline.com)
(2) Hearing loss caused by aging
Outer hair cells will gradually degenerate with age, leading to hearing loss. In this case, high-frequency outer hair cells may be more tired because they need to amplify acoustic vibrations cycle by cycle, so they often die first. Patients with age-related hearing loss usually have normal sensitivity at low frequencies, but as the frequency increases, the sensitivity gradually decreases:
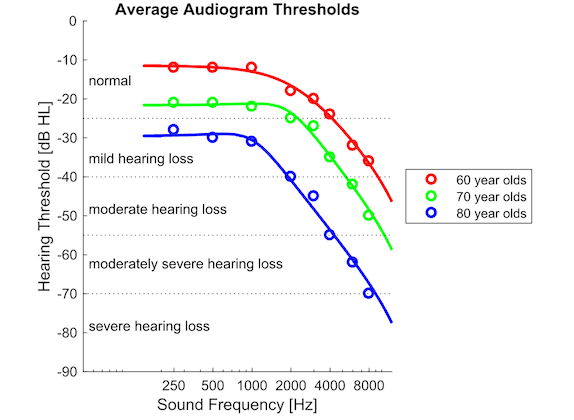
Because hearing loss can damage the patient's physical and mental health to a certain extent, affect interpersonal communication, reduce work efficiency, and increase the risk of dementia. At the same time, for those with mild to moderate hearing loss, wearing hearing aids can alleviate tinnitus. Therefore, when there is mild to moderate hearing loss, just like myopia in the eyes, you should choose otc hearing aids to wear them reasonably.

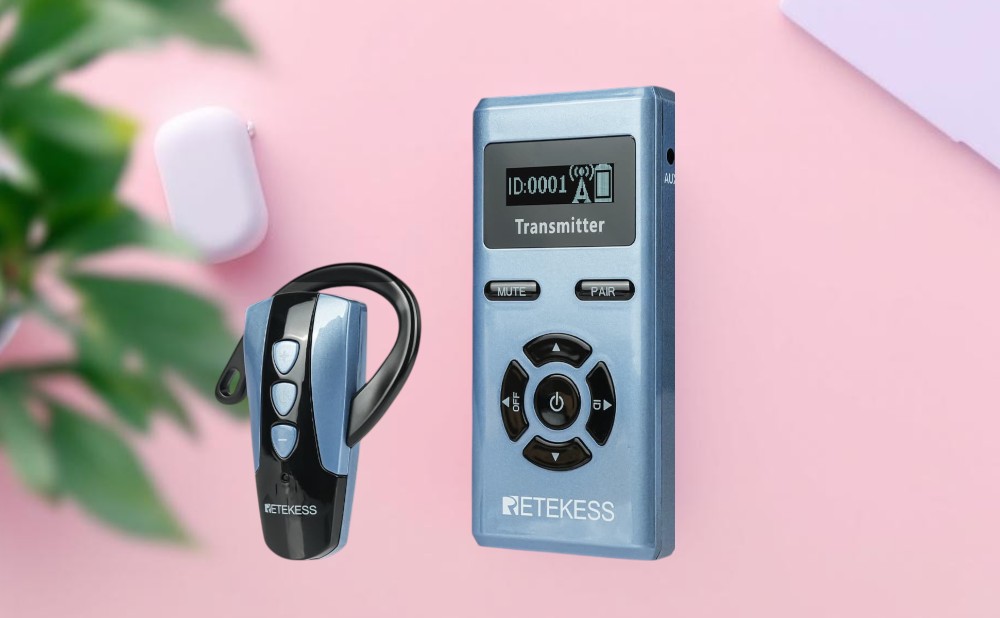
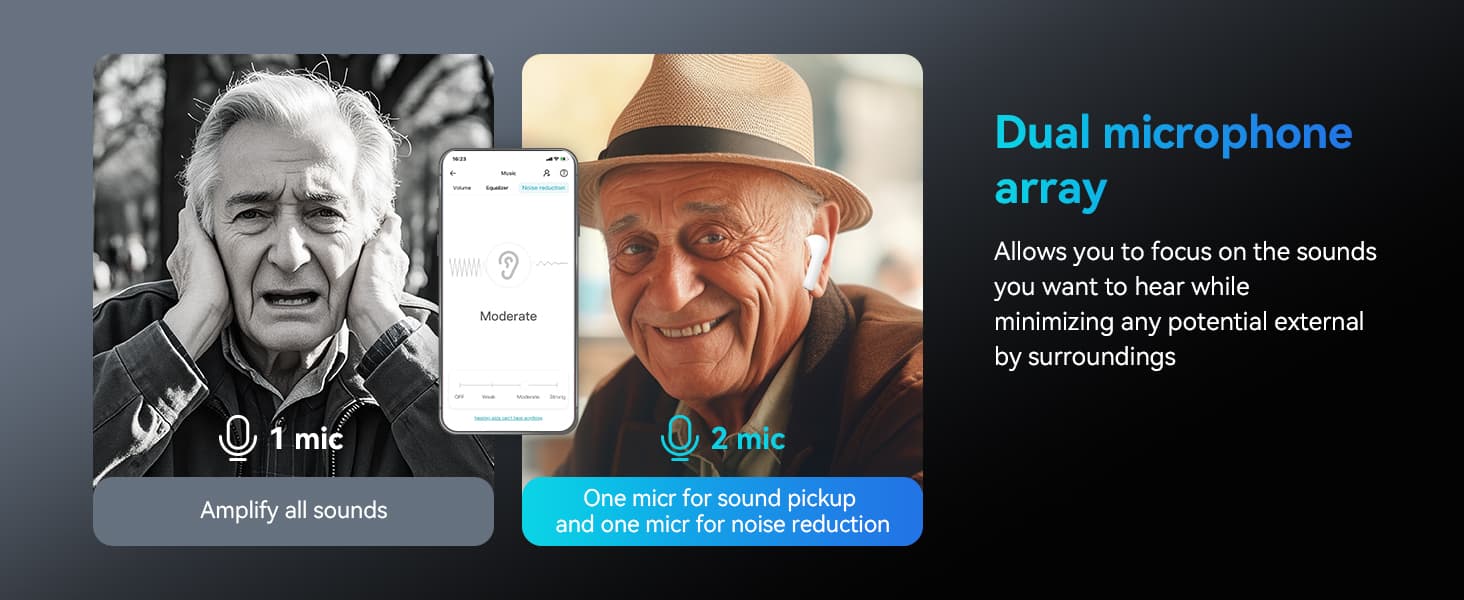
Retekess Affordable hearing aids have Bluetooth streaming function, and the self-fitting provided can automatically customize the hearing settings that suit your personal situation. The digital chip and dual microphone array provide noise reduction quality. Four modes and waterproof function make it convenient for you to use in daily life. With the charging box, it provides 48 hours of working time. The Bluetooth function is compatible with Android and Apple systems.




















Comments (0)